The Differences Between Series and Parallel Circuits
What is a Circuit
A circuit is a path that current follows when flowing. When connecting two or more components to a circuit, we either connect them in series, in parallel, or a combination of both.
A Series Circuit
A series circuit is a circuit in which all components are connected in series.
In a series connection, electrical components are put in the same path; they are connected one after the other as shown in the following diagram. Resistors R1 and R2 are in the same path.

A Parallel Circuit
A parallel circuit is a circuit in which all components are connected in parallel.
In a parallel connection, the circuit splits into different paths feeding different components and then combines back after the components as shown in the following diagram. In the following diagram, the circuit splits into two paths, the one with R1 and the other with R2.

There is another circuit called the series-parallel circuit which consists of components connected in series and in parallel. In the following diagram, resistor R1 is in series with the two resistors, R2 and R3. Whereas resistors R2 and R3 are in parallel with each other.

Voltage, Current and Resistance in Series and Parallel Circuits.
In a Series Circuit
In a series circuit, current flowing through the circuit components is the same as it follows a single path in which all components are connected.
The total current flowing in a series circuit is the same as the current flowing through each component. To find the total current flowing in a series circuit or current flowing through each component, we divide the supply voltage (voltage across the components in series) by the total resistance of the circuit components.
The voltage across each component, which is the voltage required to pass current through each component, varies from one component to another. This is because, in a series circuit, the voltage drop across each component depends on its individual resistance. However, if all components have the same resistance value, the voltage across each component will be the same.
To find the voltage drop across each component, we multiply the total current (which is the same as the current through each component) by the resistance of that specific component. To find the total voltage used in the circuit, we add up all the individual voltage drops across every component.
In a series circuit, current flowing depends on the total value of the circuit resistance. To find the total resistance of a circuit, we add up all the resistances of every component.
To find the resistance of each component, we divide the voltage across that component by the circuit current.
Example 1
Find
a. The total resistance?
b. The current flowing through resistor R1?
c. The voltage across resistor R2?

In a Parallel Circuit
In a parallel circuit, the current flowing through the components is different unless the components have the same resistance value. Since the components are in different paths, the current through each component is determined by its resistance.
To find current through each component, we divide the supply voltage by the resistance of that component. To find the total current in a circuit, we add up all the currents through every component.
In a parallel circuit, the voltage across the components is the same. This is because every component is directly connected to the supply voltage. The components are receiving the voltage.
The voltage across each component is equal to the supply voltage. The supply voltage or voltage across each component can be found by either multiplying the total current by the circuit resistance or by multiplying the resistance of each component by the current through it.
In a parallel circuit, the resistance of a component determines the current flowing through it. To find the total resistance of the circuit, we use the reciprocal formula shown in the following example. To find the resistance of each component, we divide the supply voltage by the current through that component.
There is a special method of finding total resistance of two resistors in parallel that says: For any two resistors in parallel, their total resistance can be found by dividing their product by their sum.
An example of two resistors in parallel is covered in the following two examples.
Example 2
Find
a. The total resistance?
b. The current flowing through resistor R1?

NB - Note that in (a), total resistance (R) is made the subject of the formula in order to find the total resistance.
Series-Parallel Circuit
A series-parallel circuit combines the effects of a series circuit and a parallel circuit. When finding resistance, voltage and current in a series-parallel circuit, if possible, you need to reduce the circuit into a simpler form as in the last example.
NB - Note that in the above diagram of the Series-parallel circuit, the voltage across resistor R2 or R3 (that are in parallel with each other) is not equal to the supply voltage, but it is equal to the supply voltage minus the voltage across resistor R1.
Voltage and Current Division
Voltage Divider Rule
In a series circuit, we noticed that the applied voltage is divided into as many parts as there are resistors.
More voltage is used to pass current through the components with more resistance. So for a series circuit, the voltage across any resistor in series can be found by multiplying the ratio of that resistor value to the total series resistance by the voltage or potential difference across the series arrangements as shown in the following diagram.

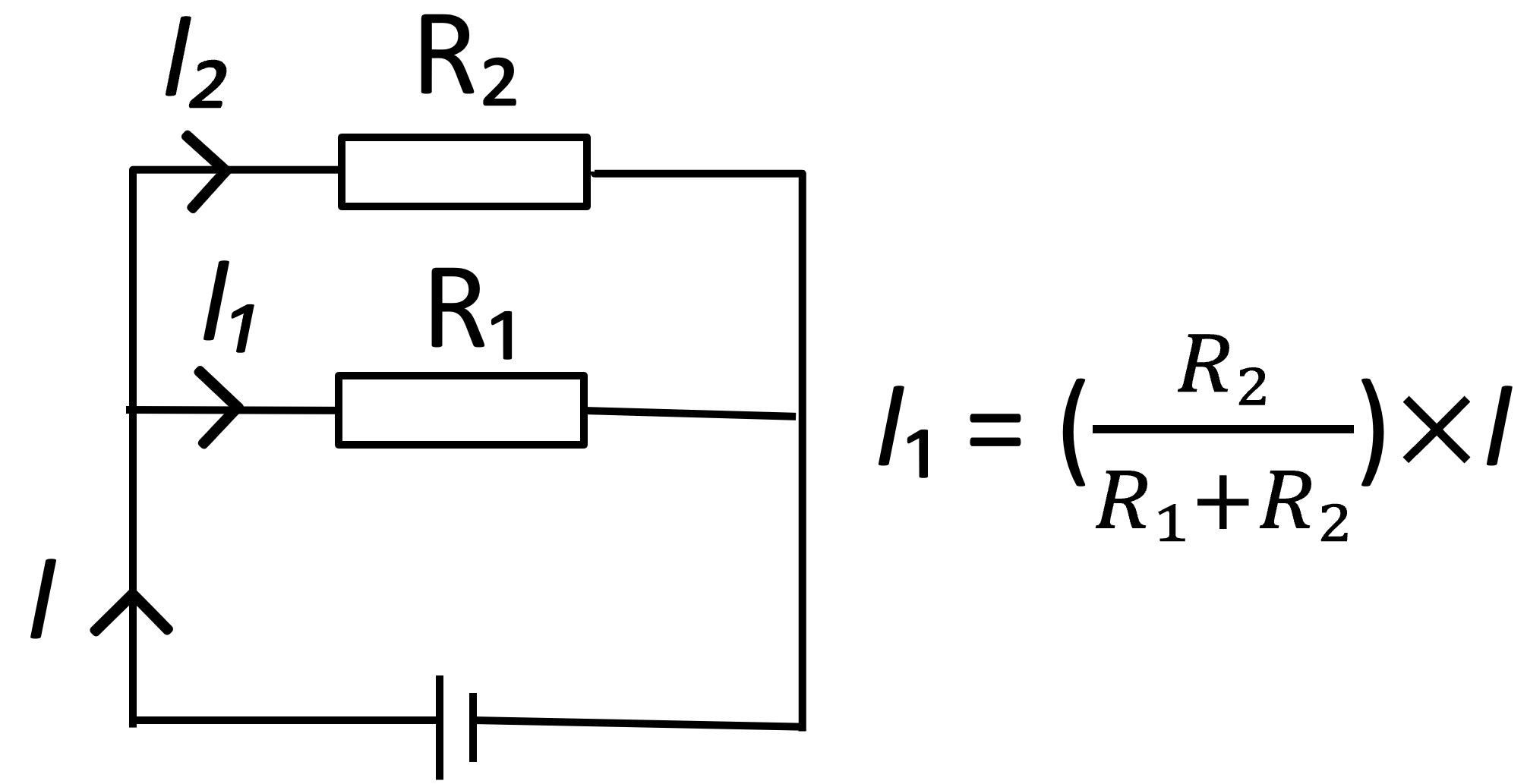
Current Divider Rule
In a parallel circuit, the current divides into as many parts as there are resistors. So in a parallel circuit, the current through any resistor can be found by using the following formula.
The formula shown below is most applicable for two resistors. For more than two resistors, there are additions to this formula.
Example 3
Find
a. The total resistance?
b. The current flowing through resistor (i) R1 and (ii) R3?
c. The voltage across resistor R2?