What is Electric Current and the Direction of Flow of Electric Current
What is Electric Current
Current is the flow of electrons in the same direction. When electrons move randomly in different directions, there is no current. And also, for electrons to flow, the circuit must be closed.
A circuit, in general, is a path that electrons follow when flowing. A circuit can be open or closed.
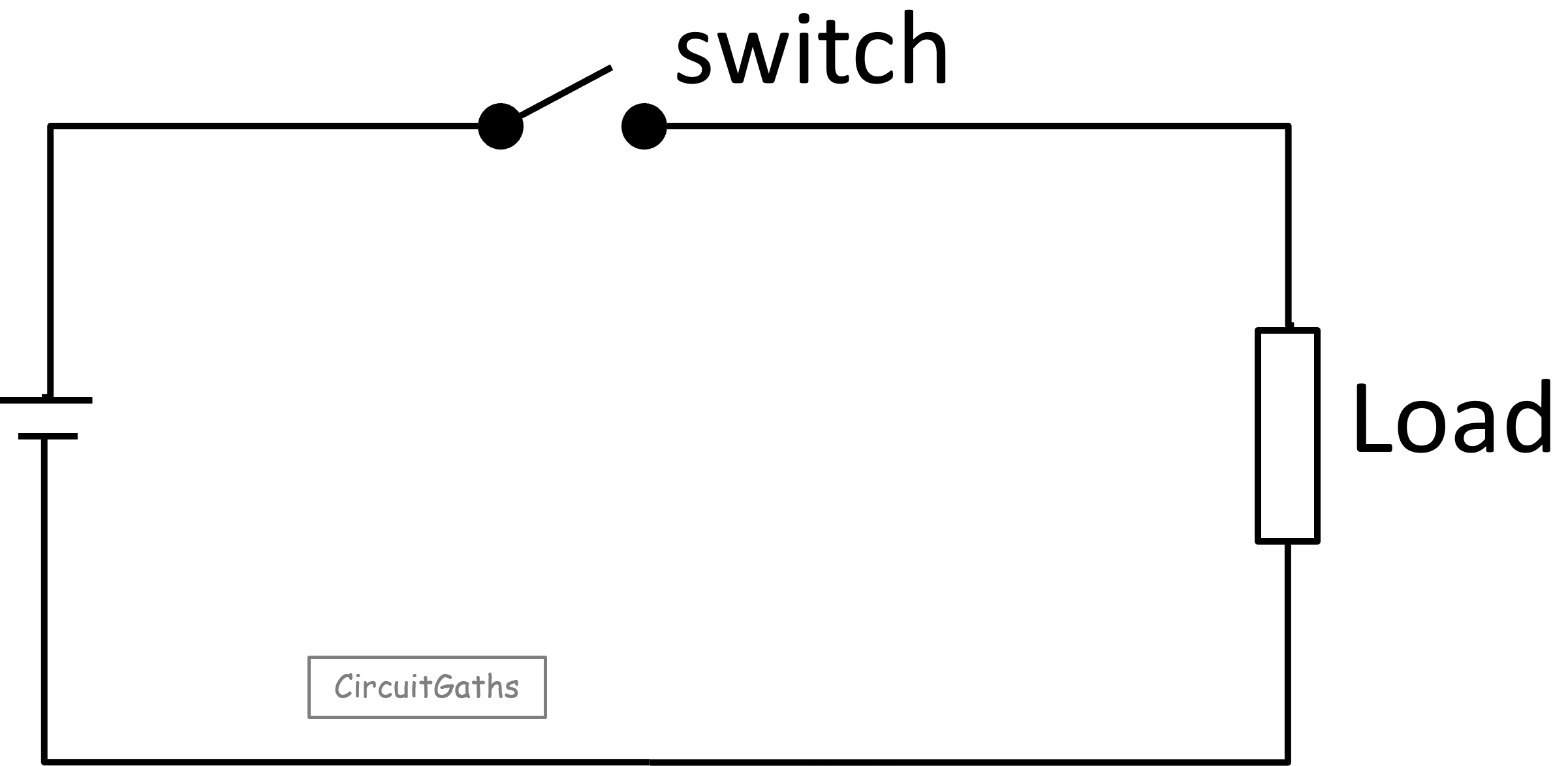
A Closed Circuit
A closed circuit is when there is a complete connection between circuit components, starting from the source (e.g a battery), lights and back to the source. All switches are in the ON position.
Switches we use at home and in industries, they just close or open the circuit. The following diagram shows a closed circuit, a switch in On position.

An Open Circuit
An open circuit is when there is a break in a circuit. It can be due to a fault or a switch in the OFF position. The following diagram shows an open circuit, with a switch in Off position.

Current is said to flow in the opposite direction to electrons. This seems confusing as in the definition above we said current is the flow of electrons. Don't worry, this is because of the two discoveries that took place in the early days of electricity.
The first discovery of current took place in the 17th century by Benjamin Franklin, a scientist. He discovered that there is something that flows inside conductors which he called current.
He went on to say that this current is due to an electric fluid flowing inside conductors in the same direction. The electric field was said to flow from the positive to the negative.
In the 19th century, J.J. Thompson, a physicist, discovered electrons, which he said are the ones that cause current or which flow.
He said they flow from negative to positive, opposing the first discovery of electric fluid. After the discovery of electrons, it was then realised that it is not electric fluid which causes current but electrons.
Before the discovery of electrons, scientists in the 17th century decided that current flows from positive to negative following the first discovery.
After the discovery of electrons, it was then difficult to change the direction because most textbooks were written and electrical symbols of components like diodes were designed to follow the first direction.
Till today the flow of current from positive to negative is accepted as the general direction of flow of current but it has nothing to do with electrons.
There are two terms that are now used to make a better understanding of current: Conventional current and Electron flow.
Conventional current is current which flows from positive to negative following the first theory. Electron flow is current which flows from negative to positive following the second theory.
Both currents seem important. Conventional current makes calculations easier because you will mostly work with positive numbers. Electron flow provides a better understanding on how electronic components work, such as diodes and transistors.
There are two types of current: Direct Current and Alternating Current
Direct Current
Direct Current is a type of current in which electrons flow in only one direction, due to the stationary positions of negative and positive polarities. Direct current is produced by solar panels and DC generators.
Alternating Current
Alternating current is a type of current in which electrons change direction of flow, flowing back and forth due to the exchanging of positions between the negative and positive polarities.
Since electrons always flow from negative to positive, when polarities exchange positions, they also alternate the direction of flow so that they continue flowing towards the positive polarity.
The exchange of positions between two polarities can be done by moving the magnetic field across a conductor. Alternating current is produced by AC generators.
How Current is Measured
Current is measured in amperes by an instrument called an ammeter. One ampere is equivalent to 6,24 × 10¹⁸ or 6 240 000 000 000 000 000 electrons passing through any point within a circuit every second.
To measure current, an ammeter is put in series with the circuit component being measured so that it counts the number of electrons passing through it in every second and displays them in amperes on the screen.

The previous diagram shows an ammeter connected in series with a circuit lamp.
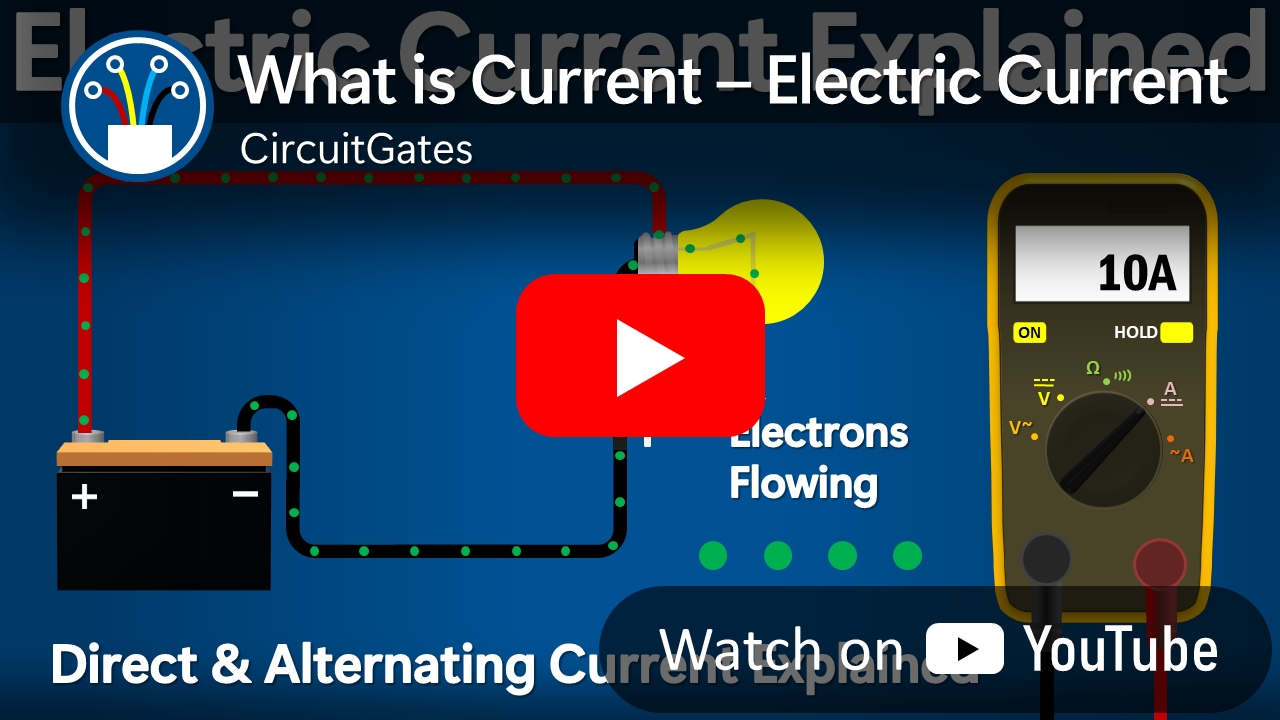
With the previous information on how current is measured, we can best define electric current as the rate of flow of electric charge since we saw that the ammeter counts the number of electrons passing through it every second.