How Electricity Works - Electric Basics Explained

Electricity involves the generation and using electrical energy. In electricity, we often talk about current, voltage, and resistance.
Current is the flow of electrons in the same direction. Resistance is the opposition given to the flow of electrons by the circuit components. Voltage is the force that pushes electrons to flow in the same direction against circuit resistance.
Everything in electricity begins with a circuit. In a circuit is where we find electrons moving, where there is resistance and where voltage pushes electrons. A circuit is defined as the path in which electrons follow when flowing. Electrical components like batteries, lamps and conductors are the ones that make up the circuit.
The Basics of Electricity
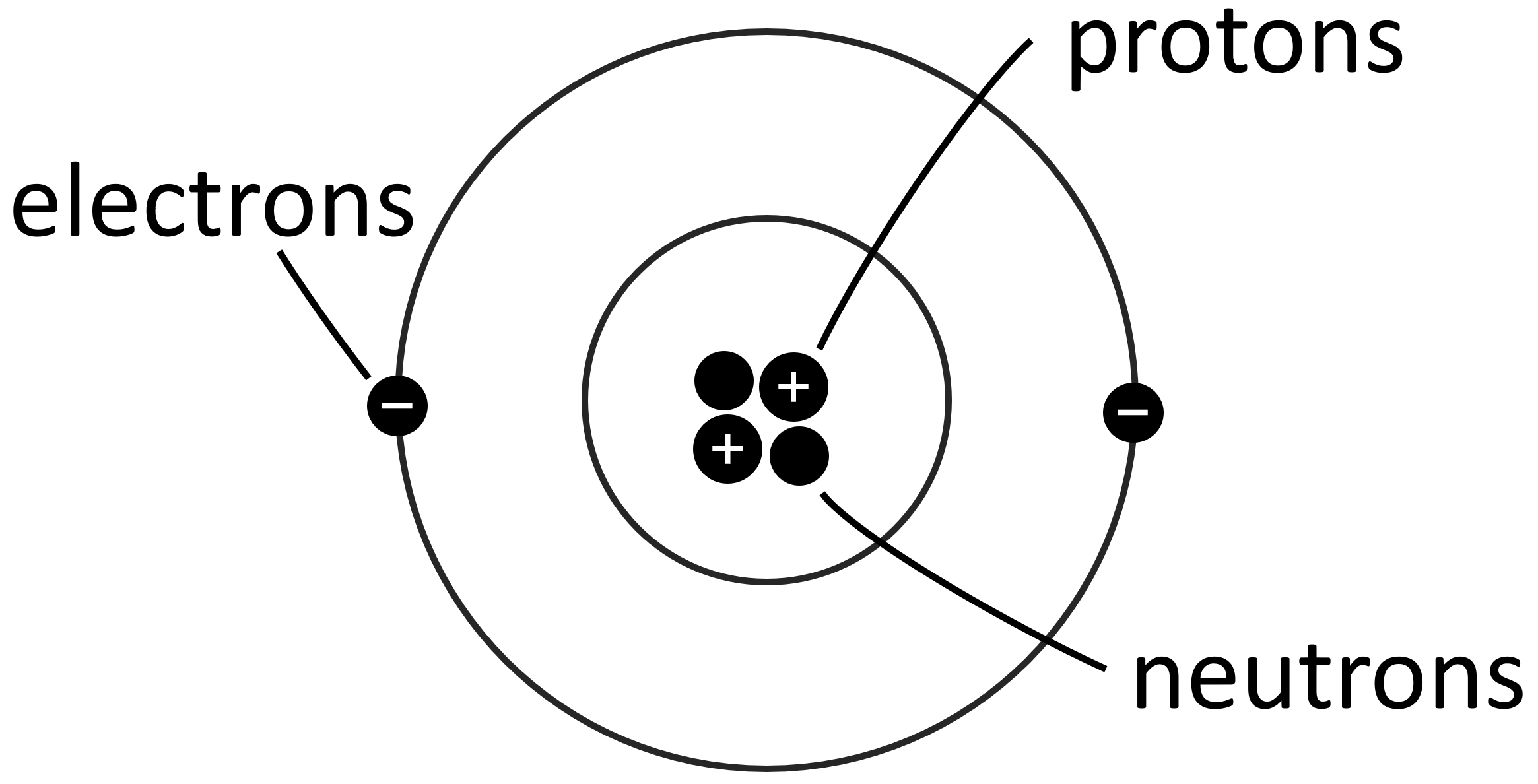
Anything on earth is made up of atoms, including conducting materials used in electrical engineering. An atom consists of protons, neutrons, and electrons.
In a material, protons and neutrons are contained inside the nucleus of atoms; they don't move. Electrons orbit around the nucleus of atoms as shown in the following diagram of a Helium atom.
Helium Atom
There are three types of materials based on the degree to which electrons are attracted by the nucleus of atoms: conductors, semiconductors and insulators.
The degree to which electrons are held by the nucleus contributes to the resistance of a material.
In conductors, electrons are loosely held by the nucleus of atoms; electrons can easily jump from one atom's shells to another. Conductors have very low resistance, they are used to conduct electricity.
In insulators, electrons are tightly held by the nucleus; they can't even jump from one atom's shells to the other. Insulators have very high resistance; they are used to cover current-carrying conductors, so that current is kept contained inside the conductor.
Semiconductors are materials that lie between conductors and insulators
What Type of Force is Voltage
If we have two bodies, one with an excess of electrons and the other with a deficit (or shortage) of electrons.
Since like charges repel each other and unlike charges attract each other, in the body with an excess of electrons there is a repellent force between electrons themselves, and in the body with a deficit of electrons, there is a force of attraction of electrons by protons.
If the two bodies are connected together through a conductor, electrons will flow from where they are in excess (or high potential) to where there is a deficit of electrons (or low potential).
The force of attraction and repulsion in the bodies constitutes voltage, just as between the positive and negative plates of a battery.
Resistance
Resistance is the opposition to flow of electrons due to bonds between electrons and protons, and the collisions between electrons as they make their way through a material.
DC and AC Electricity
Electricity is generated as either Direct current (DC) or Alternating current (AC).
Direct Current Electricity (DC)
Direct current electricity is a type of electricity in which electrons flow in only one direction. The voltage and current in direct current do not vary in magnitude. Direct current electricity is the type produced by solar panels, DC generators and stored in batteries.

Alternating Current Electricity (AC)
Alternating current electricity is a type of electricity in which electrons reverse direction of flow. The voltage and current in AC vary in magnitude regularly.
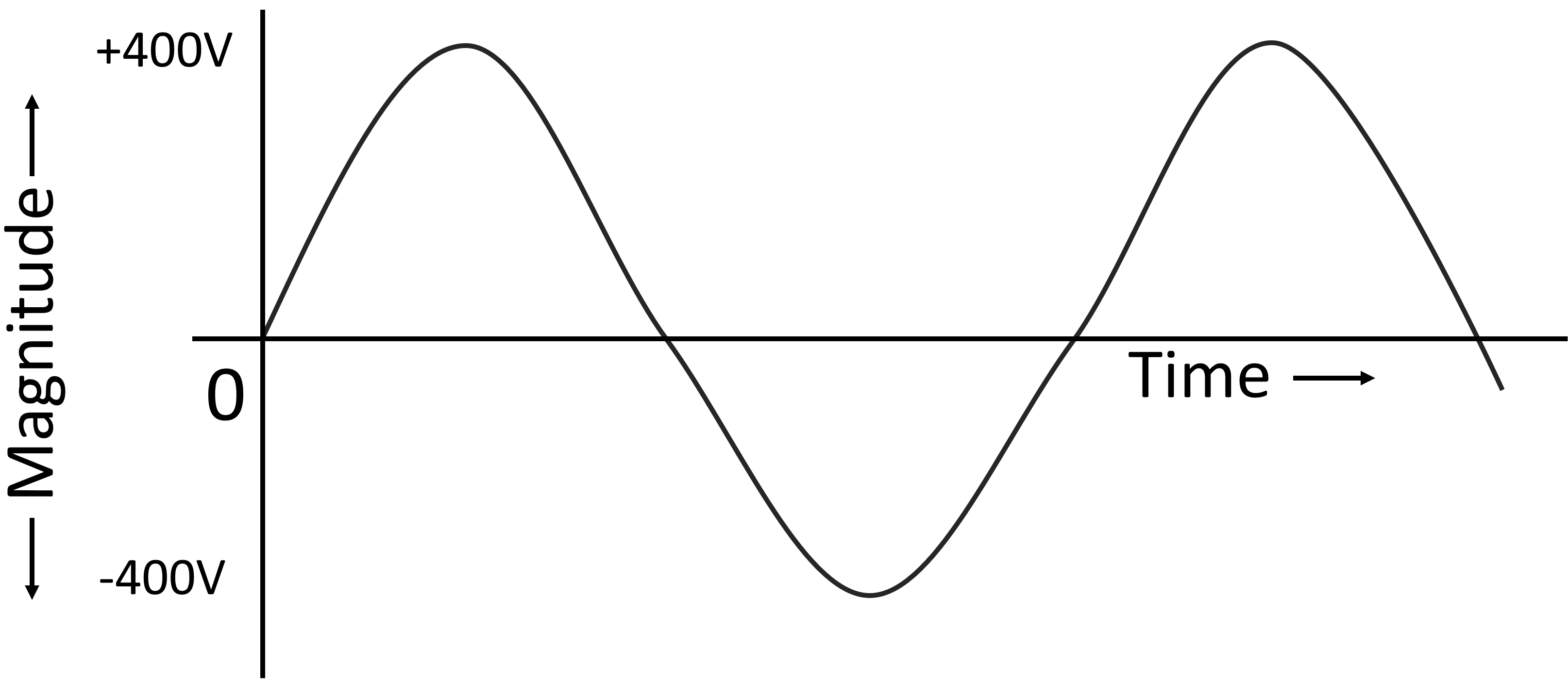
AC electricity is produced by AC generators known as alternators. In the following diagram, the positive part of the graph shows a forward direction and negative part shows a reversal in direction of AC voltage and current.
In the diagram, the curving line showing the AC values is fluctuating between zero and maximum positive and negative values; this shows that the AC voltageand current vary in magnitude.
AC is mostly used in the transmission of electrical energy because it is easy to change its characteristics. It can be easily stepped up and down with the help of transformers to reduce the loss of electricity during transmission.
DC is mostly used to power small electrical gadgets like cellphones since they contain some electronic components that need a steady supply of current and voltage.
Laptops and cellphone chargers convert AC to DC so that electronic components of these devices get a steady supply of current and voltage.
Let us look at a Circuit and Resistance Again
In electricity, electrons follow a path when flowing; this path is called a circuit.
A circuit in general is a path that electrons (current) follow when flowing. Electrical components like lamps are connected to a circuit so that electrons can pass through them.
When electrons pass through a circuit component, the materials making up the component will start to behave in other ways, which we need in electrical engineering. For example, when electrons pass through a filament lamp, the filament heats up and produces light.
A circuit can be open or closed, but to have current in the circuit, the circuit must be closed. Switches on electrical equipment are used to close or open the circuit.
A circuit possesses various properties such as resistance, inductance, capacitance, and more, that affect the flow of current. In this article, we are mainly focusing on resistance.
Resistance is a property of a circuit that opposes the flow of electrons, or it is the opposition to the flow of electrons due to bonds between electrons and protons and also collisions between electrons as they make their way through a material.
In a purely resistive circuit (a circuit with only a resistance property), resistance determines the amount of current in a circuit with respect to the applied voltage.
The Relationship Between Voltage, Current, Resistance, Power and Energy
As we have already talked about voltage, current, and resistance. Current is measured in amperes by an instrument called an ammeter.
One ampere is equal to 6,240,000,000,000,000,000 electrons passing through any given point within a circuit in every second. The ammeter counts the number of electrons passing through it in every second and displays them in amperes on the screen.
Resistance is measured in ohms by an instrument called an ohmmeter. Voltage is measured in volts by an instrument called a Voltmeter.
All the instruments we have talked about can be contained in one instrument called a multimeter. Units enable us to understand the magnitude of an electrical quantity we are working with so that the risk of electrocution is minimized.
Electrical Power and Energy
Power (P)
Power is the rate at which work is done or the rate at which energy is converted. Power is measured in watts. We can also say it is the amount of work done or energy converted in one second.
You yourself under certain circumstances, know at what time and how far you will be on a certain job; this depends with your power.
In power, we are finding out how much energy is converted in every second; the formula for power is energy divided by time in seconds.
In electrical circuits, we can also find power by the product of current and voltage flowing in a circuit.
Power = Energy ÷ Time Power = Voltage × CurrentEnergy (W)
Energy is the ability or capacity to do work. For example, you yourself know that you can complete a certain job or not; this depends on the total energy you have at that moment.
Energy is measured in joules, or more commonly in watt-seconds in electricity. 1 joule = 1 watt-second.
When finding electrical energy, we usually multiply power by time in seconds. In the formula, power is the rate at which one does a job or the rate at which one will do a job and time shows how long the job has been done or will be done, to give us energy.
Energy = Power × TimeAs we have already said, energy is measured in joules or mostly in watt-seconds in electricity, if working with a large amount of energy, the kilowatt-hour is used.
One kilowatt-hour (1 kWh) is often called a unit in electrical contexts. Most electrical supply companies charge their consumers in kilowatt-hours.